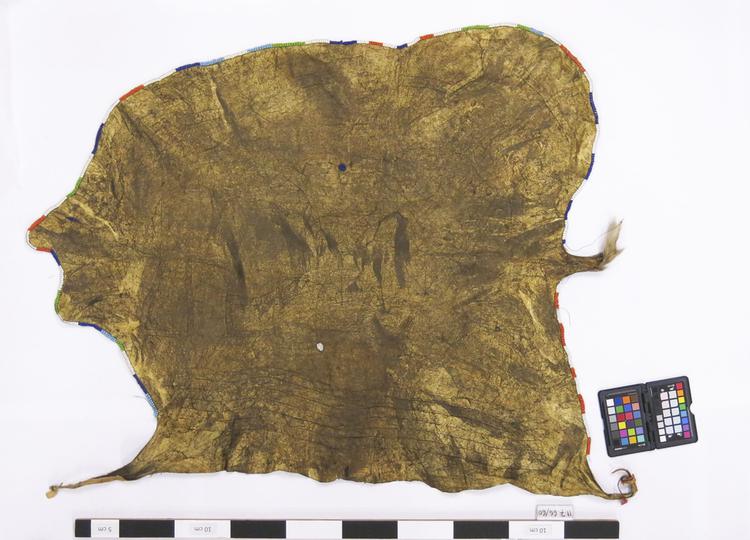
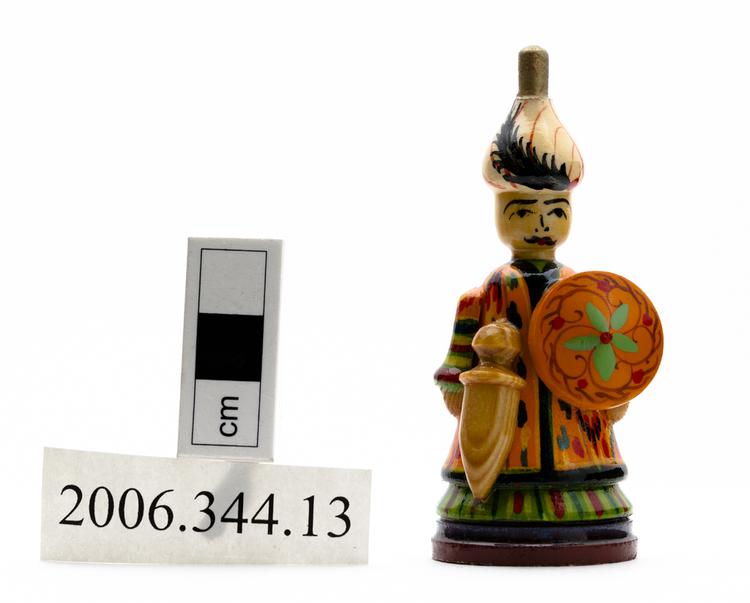
Skirt from the Hadza people of Lake Eyasi, Tanzania. The skirt is made from an animal hide, that still has areas of hair and a tail, and is decorated with white, blue, red and yellow beads.
One of three aprons worn by Hadza women in Northern Tanzania, collected by anthropologist James Woodburn in the 1960s. The Hadza are largely nomadic hunter-gatherers and have very few personal possessions. Often items of clothing are not owned by individuals, but may be requested and taken by anyone unless the item is being made good use of and worn. These aprons, made from hide and glass beads would, however, have been worn by a single individual until they reached a certain age. They will have been tied round the back, with the bead fringing at the front. It is likely that they would have been made by the women in the community (and not necessarily those directly related to the person it was intended for), perhaps reusing precious beads from another item which was no longer worn. Hadza society is largely egalitarian with variation in social status determined not by wealth or family lineage, but by age. Here we have a series of three aprons, one worn by a small child (11.7.66/62), another by an unmarried young woman (11.7.66/64). This final example is a skirt worn by a married woman, indicating the high status of married women in society.